[자료구조] 링크드 리스트 (Linked List) (Python)
1. 기본 구조와 용어
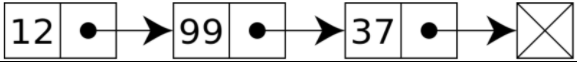
- 노드: 데이터 저장 단위(데이터, 포인터)
- 포인터: 다음이나 이전의 노드와의 연결 정보를 가지고 있는 공간
#파이썬에서는 list타입이 linked list의 기능을 모두 지원합니다.
2. 장점
- 배열의 단점인 '미리 연결된 공간을 예약해야 하는 점'을 해결할 수 있다.
- 필요할 때마다 데이터를 추가할 수 있다.
- 메모리 관리가 용이하다.
3. 단점
-배열의 장점인 index를 통한 탐색이 불가능하다.
4. Python으로 구현
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, next=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
class NodeMgmt:
def __init__(self, data):
self.head = Node(data) #시작지점을 head로 놓았음
#요소 추가하는 함수
def add(self, data):
if self.head == '': #기존에 데이터 없으면 넣으려는 Node(data)가 head값이 된다. (방어 코드)
self.head = Node(data)
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
node.next = Node(data)
#처음부터 끝까지 출력하여 확인하는 함수
def description(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(node.data)
node = node.next
#요소 삭제하는 함수
def delete(self,data):
if self.head == '':
print('해당 값을 가진 노드가 없습니다.')
return
#head 삭제하는 경우
if self.head.data == self.head:
temp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next #연결성 유지
del temp
#head 아닌 것 삭제하는 경우
else:
node = self.head
while node.next: #한번 쭉 돌기
if node.next.data == data:
temp = node.next
node.next = node.next.next
del temp
return
else:
node = node.next
def search(self,data):
node = self.head
while node:
if node.data == data:
return True
else:
node = node.next## 코드를 짜다가 python del에 대한 개념이 헷갈리는 것 같아서 좀 정리해봤다.
- del은 근본적으로 Python에서 object를 삭제하는 역할을 한다.
- 평소에는 그저 list에서 요소를 삭제할 때만 접해봐서 이런 역할만 있는 줄 알았다.
- 파이썬이 객체지향 언어인 점을 깜빡하고 있었다. 파이썬에서는 데이터와 함수가 모두 객체로 존재한다.
그러므로 integer, boolean, string, list, set, function 이런 친구들 또한 다 객체이다.
Python del to delete objects - GeeksforGeeks
Python del to delete objects - GeeksforGeeks
A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
www.geeksforgeeks.org